
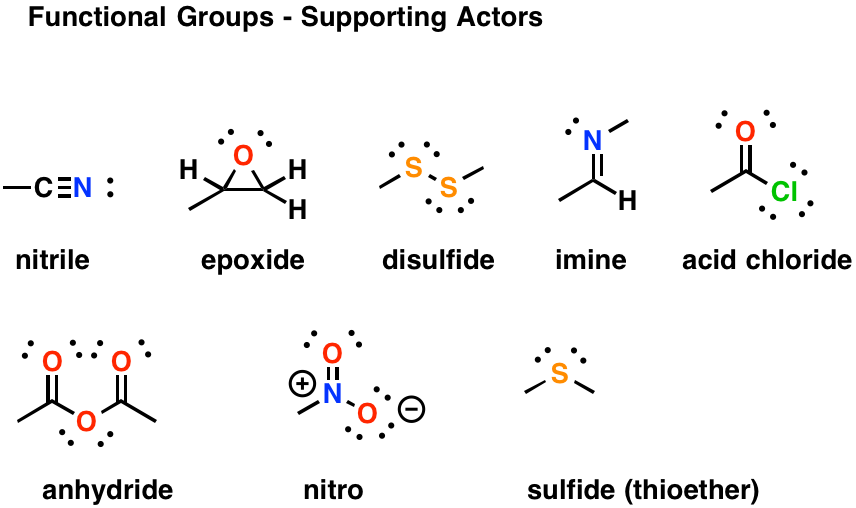
Thioether, as the name implies, is a thio (or sulfur) version of the ether.Īs we’ll see shortly, ethers have an oxygen between 2 carbon atoms. Many students won’t cover thioethers in organic chemistry, and those who do typically see them in late orgo 1 reactions.Īnytime you see the prefix ‘thio’, immediately think of sulfur. You may not be tested on this, but do recognize that if NO2 appears on your molecule, you simply add the prefix ‘nitro’.

The resonance hybrid has a partially positive nitrogen and 2 partially negative oxygens. The nitro group appears to be a very innocent neutral N + 2 O combination.īut if you draw it out, you’ll notice there’s much more going on.Ī quick Lewis structure attempt reveals 2 major resonance forms with a positive formal charge on the nitrogen and a negative charge resonating between the 2 oxygen atoms. While not required knowledge for naming and drawing early in organic chemistry, it is a tricky group that tends to confuse students when studying resonance and reactions.
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY FUNCTIONAL GROUPS FULL
Take the full halogen’s name, drop the ending and add ‘o’.įor example, iodine becomes ‘iodo’, chlorine becomes ‘chloro’.īe sure to specify the number of the carbon on which the halogen appears.įor even more watch: Naming Alkyl Halides The Nitro Functional Group -NO2 Since halogens are substituents rather than functional groups, we include their name in the prefix.
To recognize this group in organic molecules, simply look for a line to F, Cl, Br, or I This makes fluorine the smallest and most electronegative halogen, and Iodine the largest and least electronegative. Recall from the Intro to Orgo videos that electronegativity increases up and towards the right, while size increases down and towards the left. The letter ‘X’ acts as the ‘variable halogen’ and can represent any of the above. Instead, focus only on Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine and Iodine. While there are five halogens on the periodic table, I have yet to come across Astatine in over a decade of teaching Organic Chemistry. However, they are so reactive and show up so frequently in organic chemistry that we’d be remiss to skip over them. The alkyl halide is considered a substituent rather than a functional group. Ready? Let’s begin! Alkyl Halide Substituent -X R = rest of the molecule, OH = the group we’re looking at attached to the ‘rest’ of the molecule. Instead, we replace the entire parent chain with the letter R and attach the functional group to it.įor example, if I want to show you that OH is an alcohol, I will write that as R-OH. But if the focus of our discussion is a functional group, we don’t want to get distracted by all of the carbons, hydrogens, or anything else in the parent chain. What does this have to do with functional groups?įunctional groups can show up on all sorts of carbon chains. I like to think of the ‘R’ simply as the ‘ REST’ of the molecule. That ‘R’ represents the 20 different side chains.

R represents a variable group, a changeable set of atoms that we don’t care to elaborate on at this moment.įor example, if you’ve studied the 20 common amino acids you’ll notice that the common amino acid structure has a backbone and an ‘R’ on the central carbon. The letter ‘R’ pops up often in chemistry. While the R group is not a functional group at all, it’s important to discuss it before we move on. Ready to Break Down The Individual Functional Groups? Here is a quick Functional Group overview before we jump into detail Recall that if more than 1 functional group appears on a molecule, the higher priority group is named in the suffix, and the lower priority group is ‘demoted’ to substituent status and named in the prefix.įollow along with the Functional Group Priority Cheat Sheet as well as any specific functional group naming videos that are linked after the examples below. This topic is also tested on the MCAT, GAMSAT, DAT and similar exams We’ll tackle these groups from lowest to highest priority looking at While there are an overwhelming number of functional groups to consider, this guide will focus on the groups you’re most likely to come across at the beginner orgo level, along with some common groups that will show up in later (orgo 2) reactions. When classifying functional groups, we look at both the specific atoms present, as well as the manner in which they are connected to each other. Organic Chemistry Functional Groups: A Complete Guide to Recognizing, Drawing, and Naming (+ Priority Cheat Sheet at bottom)Ī functional group is a specific group of atoms that helps determine the chemistry and reactivity of the overall molecule.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
